Vapor Pressure Can Be Described as
E the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals atmospheric pressure. B the pressure exerted on the earth by the particles in the air.

Vapor Pressure Wikipedia Vapor Gas Pressure
D the pressure within the lungs during inhalation.

. The equilibrium vapor pressure is an indication of a liquids evaporation rate. O the temperature at which bubbles of vapor appear in a liquid. The temperature at which the vapour pressure of a liquid equals atmospheric pressure.
Vapor pressure relating to boiling point and heat of vaporization is the most important characteristic in the application of fats to fried food preparationTriglycerides have extremely low vapor pressures so evaporation does not occur. Ratio S p T p pure s w w. In an immiscible mixture composed of two liquids the total pressure is defined as the vapor pressure of the first liquid plus the vapor pressure of the second liquid.
Each component in a. Vapor pressure can be described as the pressure exerted on the Earth by the particles in the air. The pressure exerted by a gas above the surface of its liquid.
13 Vapor pressure can be described as A the temperature at which bubbles of vapor appear in a liquid. O the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals atmospheric pressure O the pressure exerted by a gas above the surface. Continue to heat the solution so that a boiling point at the current atmospheric pressure can be measured.
C the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals atmospheric pressure. The pressure exerted by a gas above the surface of its liquid. The temperature at which bubbles of vapour appear in a liquid.
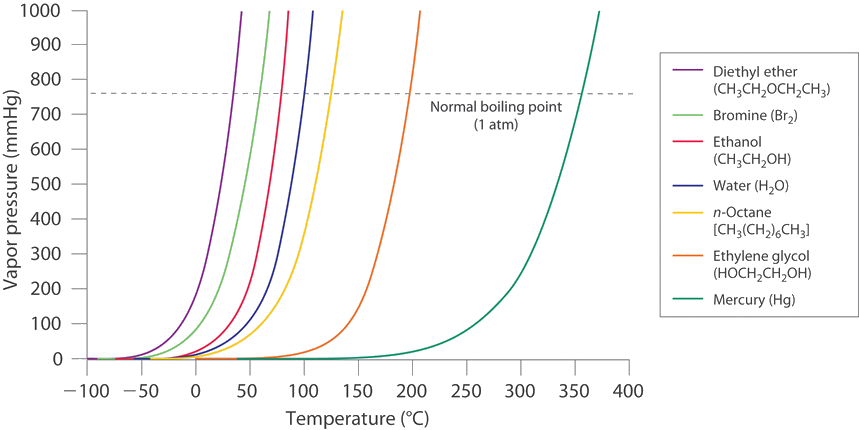
The pressure exerted on the Earth by the particles in the air. Vapor pressure at 25 o C. At one atmosphere of pressure 760 torr etc this occurs at 100 C.
B log10 P bar 3D - TKC. Vapor pressure can be described as A the temperature at which bubbles of vapor appear in a liquid. The equilibrium vapor pressure is an indication of the evaporation rate of the liquid and relates to the tendency of particles to escape from the liquid or a solid.
P p A p B Boiling Point of an Immiscible Mixture. Vapor pressure can be described as O the pressure exerted on the Earth by the particles in the air. Thus the total vapor pressure is equal to the sum of the individual pure vapor pressures.
Vapor pressure can be described as a. Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases at a given temperature in a closed system. C the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals atmospheric pressure.
On the other hand the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals atmospheric pressure is known as boiling point. Vapor pressure can sort of be described as the pressure exerted by the particles in a liquid by their kinetic energy in opposition to atmospheric pressure. That is the pressure of the vapor resulting from evaporation of a liquid or solid above a sample of the liquid or solid in a closed container.
Vapor pressure is _____. O the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals atmospheric pressure O the pressure exerted by a gas above the surface of its Iiquid. Partial esters and fatty acids have.
The pressure within the lungs during inhalation. Vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by the vapors which are present on the surface of a liquid. When the vapor pressure increases to greater than the atmospheric pressure boiling occurs.
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with the condensed phases solid or liquid at a given temperature in a closed system. EPA regulates the vapor pressure of gasoline sold at retail stations during the summer ozone season June 1 to September 15 to reduce evaporative emissions from gasoline that contribute to ground-level ozone and diminish the effects. O the temperature at which bubbles of vapor appear in a liquid.
It relates to the tendency of particles to escape from the liquid. The pressure exerted on the Earth by the particles in the air. A substance with a high vapor pressure at.
After collecting the last data point disconnect the tubing from the sidearm of the collection flask. B the pressure exerted on the Earth by the particles in the air. D the pressure exerted by a gas above the surface of its liquid.
C the temperature at which bubbles of vapor appear in a liquid. The parameters are valid from 496 to 614 K. Todays atmospheric pressure can be read from a barometer or be obtained from your TA.
153 Saturation ratio S. The vapor pressure of a liquid is the equilibrium pressure of a vapor above its liquid or solid. At pressures higher than vapour pressure water would condense whilst at lower pressures it would evaporate or sublimate.
Vapour pressure also known as vapour equilibrium pressure can be defined as the pressure exerted in a system featuring thermodynamic equilibrium by a vapour with its condensed phases solid or liquid in a closed system at a given temperature. As a liquid is heated the vapor pressure increases. Report your answer in units of kJmol.
All three states of matter. For example vapor pressure of water at room temperature is 00313 atm. Ratio of water vapor pressure pw to the saturated water vapor pressure at that temperature multiplied by 100 RH 100 p T p pure s w w.
Examples of vapor pressures are given in Table 1210 for both synthetic triglycerides and natural fats. Water is unique because no other substance occurs in _____. The vapour pressure of water is the pressure exerted by molecules of water vapor in gaseous form.
The pressure within the lungs during. The temperature at which bubbles of vapor appear in a liquid. The effect of temperature T and pressure p on equilibrium between a pure liquid and its vapor at its boiling may be described using the Clapeyron equation Eqn 1 where Δ vapS and Δ vapV are respectively the molar entropy change and the change in the molar volume associated with the liquid to vapor phase transition.
Vapor pressure can be described as A the pressure exerted by a gas above the surface of its liquid. The equilibrium vapour pressure is known to serve as an indicator of the evaporation rate of a liquid. 154 From the last two definitions we see that RH S100 ie their physical meanings are almost the same.
Air containing all of the water vapor it can hold is _____. Up to 256 cash back Vapour pressure can be described as. RVP is an abbreviation for Reid vapor pressure a common measure of and generic term for gasoline volatility.
Grams per cubic meter would be the measurement units used to describe _____. The saturation vapour pressure is the pressure at which water vapour is in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed state. Determine the heat of vaporization at a temperature of 530 K by considering temperatures 5 K from the target.
The vapor pressure of anthracene can be described by the following equation with parameters given in the table provided. D the pressure exerted by a gas above the surface of its liquid. B the pressure exerted on the Earth by the particles in the air.
Vapor pressure data points.

Vapour Pressure Definition Formula Relative Lowering Of Vapour Pressure
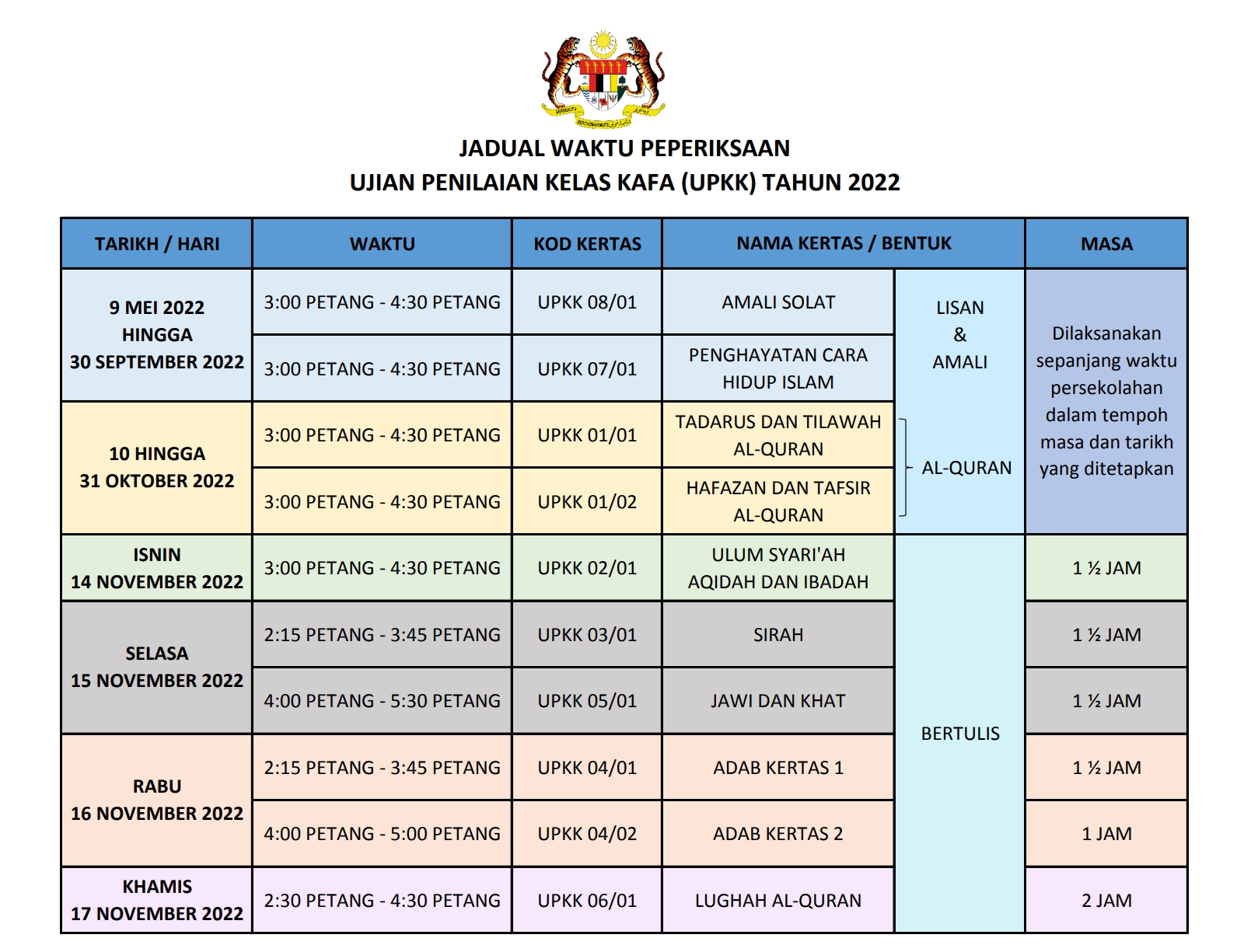
Comments
Post a Comment